Introduction, Advantages, Disadvantages And Uses Of Ceramic Pcb Boards
2021-04-16 17:11:35
Description
1. Why use ceramic circuit boards
Ordinary PCB is usually made by bonding copper foil and substrate, and the substrate material is mostly glass fiber (FR-4), phenolic resin (FR-3) and other materials, and the adhesive is usually phenolic, epoxy, etc. Due to thermal stress, chemical factors, improper production technology and other reasons during PCB processing, or due to asymmetric copper paving on both sides during the design process, it is easy to cause the PCB board to warp to varying degrees.
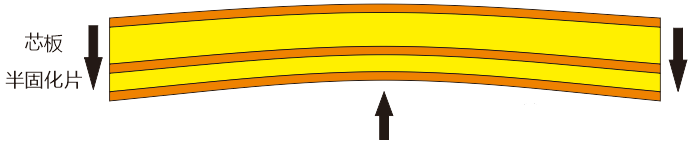
PCB warpage
And another kind of PCB substrate-ceramic substrate, due to heat dissipation performance, current carrying capacity, insulation, thermal expansion coefficient, etc., are much better than ordinary glass fiber PCB board, so it is widely used in high-power power electronic modules, aviation Aerospace, military electronics and other products.
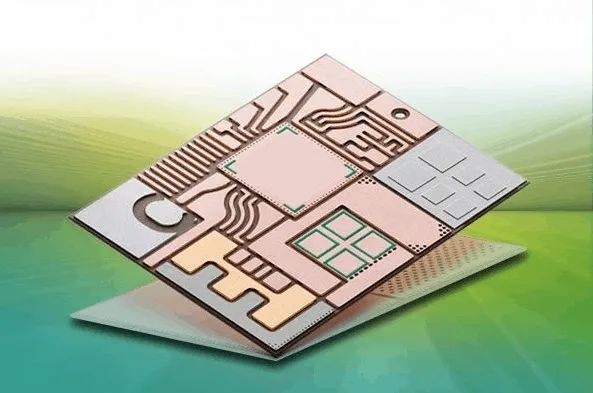
Ceramic substrate
The copper foil and the substrate are bonded together with the ordinary PCB using an adhesive. The ceramic PCB is bonded together by bonding the copper foil and the ceramic substrate in a high temperature environment. The bonding force is strong. The copper foil Will not fall off, high reliability, stable performance under high temperature and high humidity environment.
2. The main material of the ceramic substrate
Alumina (Al2O3)
Alumina is the most commonly used substrate material in ceramic substrates, because compared to most other oxide ceramics in terms of mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties, it has high strength and chemical stability, and has abundant sources of raw materials, which is suitable for various technologies. Manufacturing and different shapes. According to the percentage of alumina (Al2O3), it can be divided into: 75 porcelain, 96 porcelain, and 99.5 porcelain. The content of alumina is different, its electrical properties are hardly affected, but its mechanical properties and thermal conductivity vary greatly. The low-purity substrate has more glass phases and large surface roughness. The higher the purity of the substrate, the smoother, denser, and the lower the dielectric loss, but the higher the price.
Beryllium Oxide (BeO)
It has a higher thermal conductivity than metal aluminum, and is used in applications requiring high thermal conductivity. The temperature drops rapidly after the temperature exceeds 300°C, but its toxicity limits its own development.
Aluminum Nitride (AlN)
Aluminum nitride ceramics are ceramics with aluminum nitride powder as the main crystal phase. Compared with alumina ceramic substrate, it has higher insulation resistance, higher insulation withstand voltage and lower dielectric constant. Its thermal conductivity is 7-10 times that of Al2O3, and its coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is approximately matched to that of silicon wafers, which is essential for high-power semiconductor chips. In the production process, the thermal conductivity of AlN is greatly affected by the residual oxygen impurity content, and reducing the oxygen content can significantly increase the thermal conductivity. At present, the thermal conductivity of the current production level of 170W/(m·K) is no longer a problem.
Based on the above reasons, it can be known that alumina ceramics is still in a leading position in the fields of microelectronics, power electronics, hybrid microelectronics, and power modules due to its superior comprehensive performance.
Compare the prices of ceramic substrates of the same size (100mm×100mm×1mm) and different materials on the market: 96% alumina at 9.5 yuan, 99% alumina at 18 yuan, aluminum nitride at 150 yuan, and beryllium oxide at 650 yuan. The difference can be seen The price gap of the substrate is also relatively large.
3. Advantages and disadvantages of ceramic PCB
Advantage
Large current carrying capacity, 100A current continuously passes through the 1mm0.3mm thick copper body, and the temperature rise is about 17℃; 100A current continuously passes through the 2mm0.3mm thick copper body, and the temperature rise is only about 5℃;
Better heat dissipation performance, low thermal expansion coefficient, stable shape, not easy to deform and warp.
Good insulation, high pressure resistance, to ensure personal safety and equipment.
Strong bonding force, using bonding technology, the copper foil will not fall off.
High reliability, stable performance under high temperature and high humidity environment
Disadvantage
Fragile, this is one of the most important shortcomings, which leads to only a small area of the circuit board.
The price is expensive, and there are more and more requirements for electronic products. Ceramic circuit boards are still used in some relatively high-end products, and low-end products are not used at all.
4. The use of ceramic PCB
High-power power electronic modules, solar panel components, etc.
High frequency switching power supply, solid state relay
Automotive electronics, aerospace, military electronics
High-power LED lighting products
Communication antenna, car ignition
5. Ceramic substrate display
From the overall performance point of view, the ceramic substrate PCB is much better than the ordinary FR-4 board, but it is more expensive from the cost point of view! So, choose according to your needs!
Ceramic circuit board
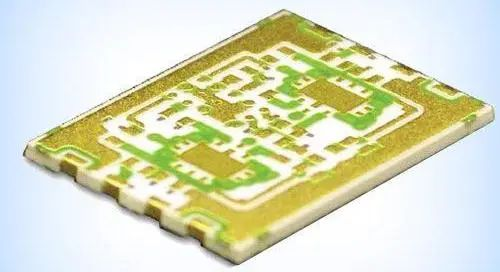
Ceramic circuit board

Ceramic circuit board
LED lamp bead ceramic substrate package
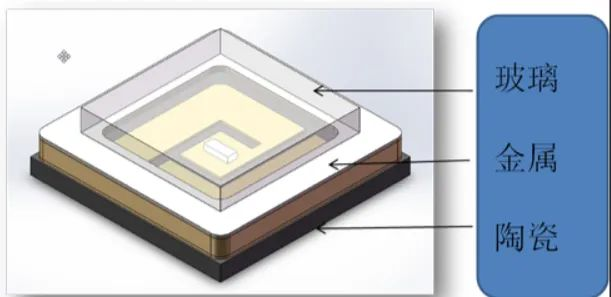
Ceramic LED lamp bead package

